
Scholar is a favourite tool of many researchers, however it can be frustrating - frequently returning overwhelming numbers of results.
Follow the slides below to learn how to get the most out of Scholar.

Scholar is not a database, it is a search engine.

Use advanced search to:

This search is targeted by title and year.

Scholar applies a ranking algorithm to the results.

Scholar does not allow structured searches (as used in databases).
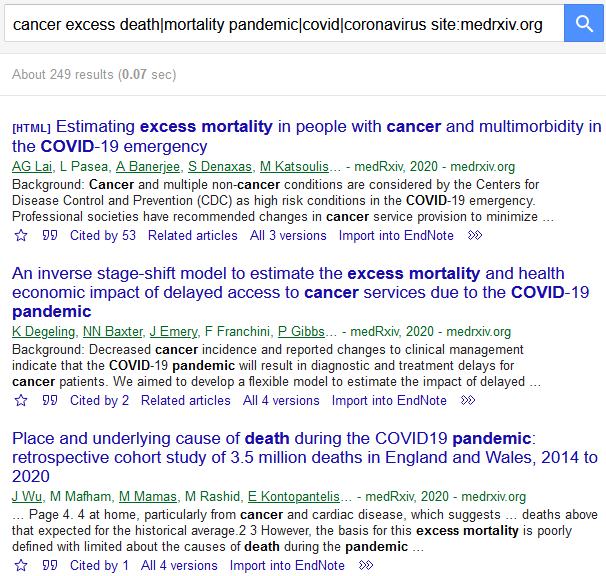
Boolean operator OR can be used for synonyms
The pipe symbol | can be used in place of OR
leave no space either side of | (on most keyboards | is above the back slash)
AND is implicit (no need to enter it)...
...but if you want to make it clear you can use the + symbol

Maximum search command is 256 characters.
Domain limits will work if Scholar indexes the site in question.
To search within a domain add 'site:domain' to the search line.
Scholar searches the full text of articles
Unlike databases like Medline there is no schedule for updating Scholar.
New articles appear when Google's bots find and index them.
So newly published articles may not be found or they may be further down the results as they have no citations or links yet.
But authors can upload their own articles to ensure they are found.
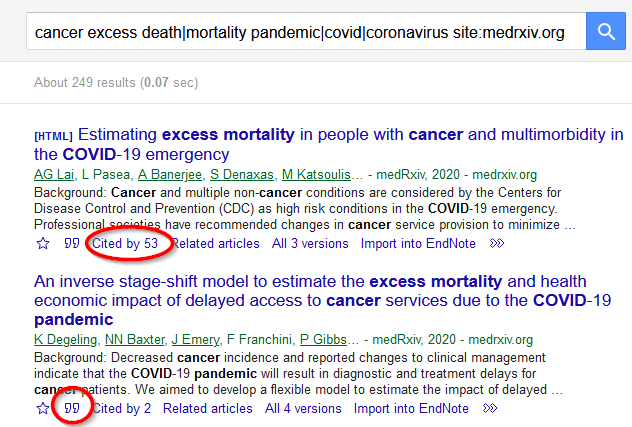
Scholar tracks citations - use the "Cited by" link to see articles which have cited this article.
You can copy the citation using the symbol under the reference.
Install the LibKey Nomad browser extension to link to full text.
OR
TIP - LibKey Nomad will link to the full text of articles on other sites too. Look for the green teardrop icon.

Now when you search you will see links to your library access.
You can create a library of articles:

Export to a reference manager program from 'My Library'

Both Google and Google Scholar may return different results depending on location, user, prior search history, computing system and over time.
For this reason they are not recommended as the prime information source for research with implied replicability, such as systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
They can be used as a supplemental source, or for research with no implied replicability or rigour.
You can also create an alert in Google Scholar to be notified of new publications.

Add these operators in the search box to focus your search.
|
Uni of Adelaide video: Find Grey Literature with Google Advanced Search (2.02 min)